Intraoperative Evaluation of Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmotic Joint
Noah H.M. Khan*, Abdul Basit Jamal and Neeshat Anjum
1Southampton General Hospital, Southampton, UK
2Laboratory Ittefaq Hospital, Lahore, Pakistan
- *Corresponding Author:
- Noah H.M. Khan
Southampton General Hospital
Southampton, UK
Tel: +442380777222
E-mail: noah_khan@hotmail.com
Received Date: July 09, 2020; Accepted Date: August 25, 2020; Published Date: September 01, 2020
Citation: Khan NHM, Jamal AB, Anjum N (2020) Intraoperative Evaluation of Distal Tibiofibular Syndesmotic Joint. J Rare Disord Diagn Ther Vol.6 No.5:10. DOI: 10.36648/2380-7245.6.5.207
Clinical Image
Acutely injured ankles are one the most common skeletal injuries and account for 9% to 18% of all the fractures treated in emergency departments [1,2]. These injuries can involve the distal tibiofibular syndesmosis that can lead to instability requiring specific treatment beyond fixation of the fracture. The syndesmosis is usually injured by external rotation of the ankle with hyper-dorsiflexion of a pronated or supinated foot [3]. These injuries occur in up to 10% of ankle sprains and up to 23% of all ankle fractures [4].
Pre-operative radiographic measurements such as tibiofibular overlap, tibiofibular clear space, medial and superior clear space are of little value in detecting syndesmotic injury because these depend on ankle rotation during radiography [5]. Jenkinson et al concluded that intraoperative fluoroscopic stress examination increases the rate of detection of syndesmotic injury [6]. A biomechanical cadaveric study concluded that intraoperative hook test is more reliable, because of the greater displacement when performing this test, than the external rotation stress test [7].
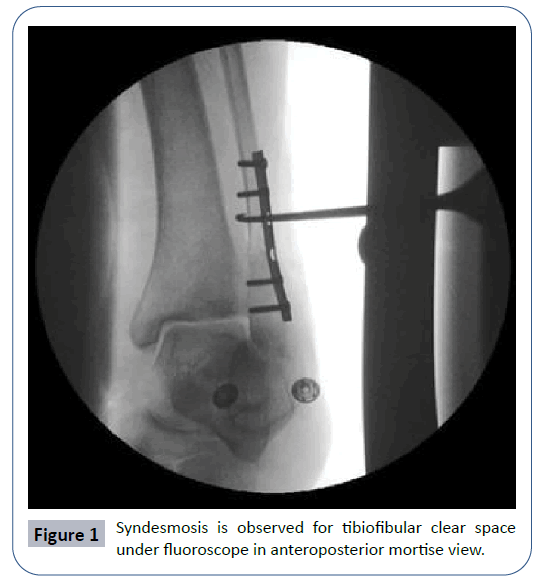
Frederic J. Cotton first described the hook test to test the integrity of ankle syndesmosis intraoperatively [8]. After appropriate fixation of fibula, to perform this test a bone hook is used to distract the fibula in sagittal plane by applying manual force. A counter force is applied to tibia to prevent tibial motion. Syndesmosis is observed for tibiofibular clear space under fluoroscope in anteroposterior mortise view (Figure 1). Tibiofibular clear space exceeding the 5 mm indicates an unstable syndesmosis [7,8].
References
- Miller AN, Paul O, Boraiah S, Parker RJ, Helfet DL, et al. (2010) Functional outcomes after syndesmotic screw fixation and removal. J Orthop Trauma 24: 12-16.
- Court-Brown CM, Caesar B (2006) Epidemiology of adult fractures: A review. Injury 37: 691-697.
- Norkus SA, Floyd RT (2001) The anatomy and mechanisms of syndesmotic ankle sprains. J Athl Train 36: 68-73.
- Purvis GD (1982) Displaced, unstable ankle fractures: Classification, incidence, and management of a consecutive series. Clin Orthop 165: 91-98.
- Nielson JH, Gardner MJ, Peterson MGE, Sallis JG, Potter HG, et al. (1985) Radiographic measurements do not predict syndesmotic injury in ankle fractures: An MRI study. Clin Orthop 436: 216-221.
- Jenkinson RJ, Sanders DW, Macleod MD, Domonkos A, Lydestadt J, et al. (2005) Intraoperative Diagnosis of Syndesmosis Injuries in External Rotation Ankle Fractures: J Orthop Trauma 19(9): 604-609.
- Stoffel K, Wysocki D, Baddour E, Nicholls R, Yates P, et al. (2009) Comparison of two intraoperative assessment methods for injuries to the ankle syndesmosis. A cadaveric study. J Bone Joint Surg Amm 91: 2646-2652.
- Cotton F (1869-1938) Fractures and joint dislocations. Philadelphia, PA: W. B. Saunders Company, USA. p. 654.
Open Access Journals
- Aquaculture & Veterinary Science
- Chemistry & Chemical Sciences
- Clinical Sciences
- Engineering
- General Science
- Genetics & Molecular Biology
- Health Care & Nursing
- Immunology & Microbiology
- Materials Science
- Mathematics & Physics
- Medical Sciences
- Neurology & Psychiatry
- Oncology & Cancer Science
- Pharmaceutical Sciences